VirtualBox: An Alternative to VMware Workstation Pro
The idea of virtualization started during the
mainframe days in the late 1960s and early 1970s. IBM was the first to apply virtual
machines in the commercial environment. Different companies then followed and
introduced their own version. In 1999, a company called VMware began selling
their virtualization software called VMware Workstation. And in 2010, Oracle
Corporation took over development of VirtualBox after purchasing Sun
Microsystems. In today’s modern IT industry, both VMware and Oracle are market
leaders in virtualization.
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization uses a software to create a
virtualization layer over an actual hardware to abstract the host machine and
its operating system from the guest machines. This layer allows a single
computer’s resources (processors, memory, storage and more) to be distributed
into multiple virtual instances of a computer system. These virtual instances
are commonly called virtual machines (VMs). These virtual machines can run
different operating systems or applications and can interact independently while
just having a portion of the resources of a single host machine.
There are many reasons why virtualization is being
utilized by companies and organizations. Some of the key benefits of
virtualization includes resource optimization, easier management, maximizing
uptime, minimal downtime, easy migration, and faster provisioning. With today’s
enterprise level computer resources, without virtualization, server resources would
be underused. By virtualizing the server resources, we can create multiple
virtual machines which allows us to fully utilize the physical server’s
computing capacity.
Hypervisors
The virtualization or abstraction layer on top of the
host machine where you execute VMs is created with a hypervisor. A hypervisor
is a program that creates and runs virtual machines. It is also sometimes
called a virtual machine monitor (VMM). The hypervisor pools all the physical
hardware resources and virtually shares its resources between existing guests
or to new virtual machines. Hypervisors are split into two types: type 1 and
type 2. Type 1 or bare metal hypervisor is installed directly on the host’s
hardware which takes the place of a host operating system. This type of
hypervisor is commonly seen in enterprise data center or virtual server
scenarios. The type 2 or hosted hypervisor is installed on top of an existing
operating system. The most common examples of type 2 hypervisors are VirtualBox
and VMware.
What is VirtualBox?
VirtualBox is Oracle’s x86 and AMD64/Intel64 cross-platform
virtualization software that can run multiple virtual machines on Mac OS,
Windows, Linux, or Oracle Solaris systems. It is an open-source software and
freely available under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL)
version 2. It is a high-performance product with a lot of features that is
suitable for enterprise as well as home use. Currently it supports multiple
guest operating systems which includes Windows, DOS/Windows 3.x, Linux, Solaris
and OpenSolaris, OS/2, and OpenBSD. VirtualBox is a community effort wherein
everyone is encouraged to contribute. It is constantly being developed with
frequent releases and Oracle guarantees that the product achieves professional
quality criteria.
These are the minimum requirements in order to run VirtualBox on your machine:
- AN x86 hardware.
Any recent Intel or AMD processor.
- Memory. Depending on
the guest operating system but at least 512 MB of RAM plus the memory needed to
run the host operating system. Always check the minimum RAM requirements of the
guest operating system you intend to run since it will refuse to install if
provided with less.
- Hard Disk Space. An
install of VirtualBox will only need about 30 MB of hard disk space. The
virtual machines own hard disk storage will depend on the type of guest
operating system.
- Operating System. A supported host and guest operating system.
VirtualBox Features
Portability
VirtualBox
can run on both 32-bit and 64-bit host operating systems. It is very portable
since it is functionally identical on different host OS. It also uses the same
file and image formats on all of the host platforms. This means a virtual
machine created on Windows can also be ran under Linux.
Importing
and exporting virtual machines is also available in VirtualBox using the Open
Virtualization Format (OVF). OVF from different virtualization software can
also be imported into VirtualBox. This functionality is even extended into
exporting and importing VMs into the cloud for users of Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure.
Guest
Additions
VirtualBox
comes with Guest Additions to improve guest operating systems performance and
integration and communication with the host machine. Guest additions are
provided as an image file and can be found in the installation directory of
VirtualBox. This image file is usually installed into a virtual machine after
the guest OS is installed. Once installed, it provides a lot of features which
includes mouse pointer integration, shared folders, better video support,
seamless windows, shared clipboard, time synchronization and automated logins.
Hardware Support
VirtualBox offers
different hardware support, one of them is guest multiprocessing which allows
VirtualBox to provide up to 32 virtual CPUs to each VM regardless of how many
CPU cores the host have. VirtualBox also provides USB device support which
means that you can easily connect USB devices to virtual machines without
installing drivers on the host. The other hardware support includes full ACPI
support, multiscreen resolutions, built-in iSCSI support and PXE network boot.
Snapshots
A snapshot
is a saved state of a virtual machine at a specific point in time. Snapshots
are usually used for backup and recovery. With VirtualBox you can save multiple
snapshots of your virtual machine as long as there is enough disk space on the
host machine.
Remote Machine Display
VirtualBox comes with an extension interface called
VirtualBox Remote Desktop Extension (VRDE) which allows high-performance remote
access. VirtualBox is able to remotely display virtual machines, which means
users are able to run a virtual machine in one host computer and then have it
displayed on a second computer. Aside from having support to Windows’ Remote Desktop
Protocol (RDP), it also comes with a full client USB support and an extensible
RDP authentication.
What is VMware Workstation Pro?
VMware Workstation Pro is VMware’s 64-bit hosted
hypervisor that has a lot of virtualization features for desktops. This can run
multiple virtual machines on most 64-bit Windows or Linux host operating
systems with x86 hardware and intel64/AMD64 processors. In addition, it can
also run multiple containers or Kubernetes clusters. Currently, Workstation pro
supports multiple 32-bit and 64-bit guest operating systems which includes
Windows, Linux, Solaris, FreeBSD, and various other Linux Distros.
These are the minimum requirements in order to run VMware Workstation Pro on your machine:
- AN x86-based hardware.
Any 64-bit processor released in 2011 or later. A 1.3GHz or faster core speed.
- Memory. Total memory
needed by the host machine includes the memory to run the host operating system,
the guest operating system, and the applications in both the host and guest
machines. The recommended memory size is 4GB and above while the required
minimum memory is 2GB.
- Hard Disk Space. The
basic install of VMware Workstation Pro requires 1.5GB of free disk space. In
addition, it is recommended to provide at least 1GB free disk space for each guest
machine in order to run the guest operating system and the application
software.
- Operating System. A
supported host and guest operating system.
VMware Workstation Pro Features
Broadest Support of Guest Operating Systems
VMware Workstation Pro supports hundreds of either
32-bit or 64-bit operating system. It can also run applications on mobile operating
systems like Android-X86.
VMware Tools
VMware Workstation Pro comes with VMware Tools which
is installed after the guest operating system is completely installed. VMware
Tools are utilities that improves a virtual machine’s performance and provides many
features. Some of these features include faster graphic performance, the unity
feature, shared folders, improved mouse performance, and scripting to automate
guest operating system operations.
Hardware Support
VMware Workstation Pro allows you to create virtual
machines with up to 16 virtual processors, and 64GB of memory. It also has SCSI
device support which means you can use SCSI devices on virtual machines without
having to install drivers in the host machine. Other hardware support includes
support for IDE drive, USB port, networking, and sound.
DirectX
11
VMware Workstation Pro provides accelerated graphics and
gaming support. With the DirectX 11, you are able to allocate 8GB of VRAM to
guest VMs which will improve gaming experience and performance of 3D apps.
Containers and Kubernetes
VMware Workstation Pro now comes with a unique command-line utility called vctl. Using vctl allows you to manage and run OCI container images. It also provides support for KIND which is used to run local Kubernetes clusters.
VirtualBox vs VMware Workstation Pro
The following video will provide a detailed comparison
of VirtualBox and VMware Workstation Pro.
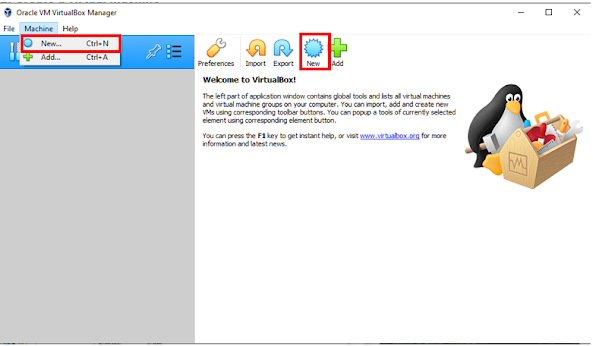
Installing VirtualBox
You now know the different features of VirtualBox and
how it compares to VMware Workstation Pro. Next thing to do is to try out and install
VirtualBox. The process of installing VirtualBox in supported operating systems
is mostly similar. Here are the steps to install VirtualBox
in Windows:
1. Download the latest version of VirtualBox for Windows in the official site virtualbox.org
2. Select Windows hosts among the available packages. A file will then be downloaded.
8. Click finish to start Oracle VM VirtualBox.
Conclusion
Both VirtualBox and VMware Workstation Pro have some
features that the other virtualization software may not have. VMware Workstation
Pro has an advantage in terms of performance and 3D graphics. However, the
difference between the two is not that noticeable and VirtualBox does have a
lot of features that are comparable to VMware Workstation Pro. One of the
advantages of VirtualBox is that it is open source and free to use. So, if you
want to do virtualization without needing to buy a license and still get
features close to VMware Workstation Pro, VirtualBox would be a great
alternative.
Resources
VMware vs VirtualBox: Comprehensive Comparison

Comments
Post a Comment